When it comes to BIM (Building Information Modeling), seven primary dimensions are currently employed throughout a project’s life cycle. However, among all the BIM levels, 3D BIM modeling stands out as the fundamental cornerstone for any project following the BIM process.
Universal concept of 3D Modeling
Definition: What does 3D modeling mean?
Before delving into 3D BIM, it is important to learn about the universal concept of 3D Modeling. 3D modeling is a technique in computer graphics for producing three-dimensional representations (x, y, and z). It is the process of creating 3D objects and surfaces, manipulating polygons, faces and edges.
Many industries use these models, i.e., film industry, architecture industry.
Regarding the architecture industry, the engineering design process is very iterative, whenever a change to the design is made, the visuals need to be changed as well. Using this format, it is easy for designers and architects to see how the changes can affect the overall design.
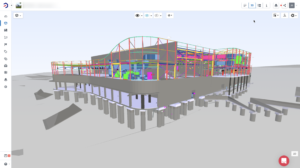
3D in Building Information Modeling (BIM)
What is 3D BIM in Design and Construction?
In realms of high complexity and visualization, such as design and construction, the application of three-dimensional modeling is highly appreciated, and 3D BIM is considered the most well-known dimension of Building Information Modeling.
The BIM dimensions include 3D BIM in level 2. The production of this type of models of structures, visualizations, and walkthroughs are all part of 3D BIM. It also includes the production of models using point cloud data from laser scanners. Another facet of that BIM level is the synchronization of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing data with 3D architectural models. Additionally, it allows for the clash detection and interference studies between disciplines.
Because these models with BIM technologies are faster, more accurate, and more coordinated with other disciplines, it opens up new possibilities. When a designer or a construction professionals makes a change to a building element or geometry in one view, such as a plan, section or elevation, the Building Information Modeling tool coordinates the change in all other views.
You can work with building elements, create conceptual models, objects, and geometries, and use computational and parametric design with 3D BIM.
3-Dimension view allows all project’s team members to work together efficiently to model and solve common structural issues. Every related information and data is stored in the Building Information model, so it becomes easier to handle concerns in the future.
What is the application of 3D BIM technology in the Catenda Hub platform?
The process of 3D BIM involves generating both geometrical and non-geometrical information and then sharing this data within a common data environment (CDE).
Catenda Hub is a Common Data Environment (CDE) that helps designers and construction actors to effectively manage their BIM projects, design planning and collaborative process in digital environment.
Our open standards-based cloud platform offers a powerful 3D viewer, allowing a team of designers, architects, structural engineers and other users to view the models and collaborate seamlessly. Its intuitive interface ensures that navigating through and examining these 3D BIM models is a straightforward and user-friendly experience.
What are the solid benefits of using 3D models?
The built asset sector has been progressively shifting from 2D to 3D BIM. It’s clear that the use of 3D BIM unquestionably offers numerous benefits for BIM projects.
- Visualization: The full project is fully visualized in 3D geometry, aiding in better understanding;
- Design and Planning: 3D models facilitating accurate planning, allowing professionals to visualize and refine their designs before implementation.
- Collaboration: Design expectations are communicated and shared more efficiently among designers, architects and various participants.
- Better coordination: Complex ideas can be better coordinated and communicated through 3D models within several teams in digital environment, bridging the gap between technical professionals and non-experts.
- Cost and Time Savings: Due to complete transparency from the start, there are fewer instances of rework and revisions, resulting in time and cost saving.
- Digital Twin Creation: 3D models serve as the foundation for creating digital twins, enabling real-time monitoring, analysis, and management of physical assets.
What is 3D BIM software you should use in your project?
In the evolving landscape of BIM software, determining the most relevant tool to facilitate the collaborative project process is both an opportunity and a challenge. According to specialists from BIM Corner, here is a list of recommended BIM software that you can consider for your next projects.
- Archicad
- Autodesk BIM 360
- Autodesk Civil
- Autodesk Navisworks
- Autodesk Revit
- Catenda Hub
- dRofus
- Dynamo
- Gemini Terrain
- Grasshopper
- MagiCAD
- Rhinoceros
- Simple BIM
- Solibri
- Trimble
The decision can be influenced by your prioritization of functional characteristics, user requirements and cost. Given the multitude of software options involved in your projects, tools that support IFC files (Industry foundation classes) and strictly adhere to open standards are crucial for unlocking a seamless workflow and facilitating a collaborative process.
Additionally, an increasing number of stakeholders in many construction firms are navigating BIM models using augmented and virtual reality. Therefore, BIM software such as Vrex should be taken into consideration for effective communication in the digital environment, leveraging the support of VR technology.